What is SoftEther VPN, and why should you care?

SoftEther (or Software Ethernet) VPN is a free, open-source VPN software suite created at the University of Tsukuba in Japan that’s been praised for its flexibility and security.
In this article, we’ll explain how SoftEther works, its strengths and weaknesses, and how it compares to more familiar options like OpenVPN and WireGuard to help you decide if it’s the right VPN solution for you.
How does the SoftEther VPN protocol work?
SoftEther has its own native protocol that establishes secure VPN connections using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) / Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption over Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 443, the same port used by standard HTTPS traffic.
Unlike most VPN protocols, which rely on dedicated ports, SoftEther’s approach allows it to blend in with normal web traffic, making it difficult to detect or block.
In addition to its native protocol, SoftEther also supports multiple other VPN protocols, including OpenVPN, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with Internet Protocol Security (L2TP/IPsec), and Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP), providing flexibility for various use cases.
Key features and benefits of SoftEther VPN
Here’s a quick overview of the main features and advantages of SoftEther VPN.
High level of security
SoftEther VPN provides strong protection using 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption, a widely trusted method that scrambles your data so it can’t be read by third parties even if they intercept it. The protocol also supports 128-bit AES and three additional encryption algorithms that are now outdated and considered insecure: 128-bit Rivest Cipher 4 (RC4), 56-bit Data Encryption Standard (DES), and Triple-DES.
It offers multiple ways to verify users, such as Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) certificates and Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS ) / Windows New Technology (NT) Domain authentication, ensuring that only authorized users can access the VPN. Additional measures, including packet filtering and configurable security policies, help prevent unauthorized access and attacks like man-in-the-middle intrusions, keeping the user’s traffic secure across networks.
Compatibility across operating systems
SoftEther VPN supports multiple operating systems. Its client, bridge, and server software are compatible with Windows and Linux, while the bridge and server software additionally work on macOS, FreeBSD, and Solaris.
Android and iOS devices can connect to a SoftEther VPN server using supported protocols like L2TP/IPsec.
Performance and speed benchmarks
SoftEther VPN is designed for high-speed performance with minimal resource consumption. The protocol employs a parallel transmission mechanism, allowing multiple SSL VPN tunnels to operate concurrently, which enhances throughput, especially over slow or congested networks.
Additionally, SoftEther VPN supports Quality of Service (QoS), prioritizing high-importance packets like VoIP traffic to ensure consistent performance.
Open-source flexibility and community support
SoftEther VPN is an open-source project, which means anyone can examine its code, look for security vulnerabilities, and suggest improvements. (This is not a unique feature of SoftEther: Other open-source protocols include ExpressVPN’s proprietary Lightway protocol, WireGuard, and OpenVPN.)
This transparency allows users and developers worldwide to participate in SoftEther’s development, helping maintain the software’s reliability and security.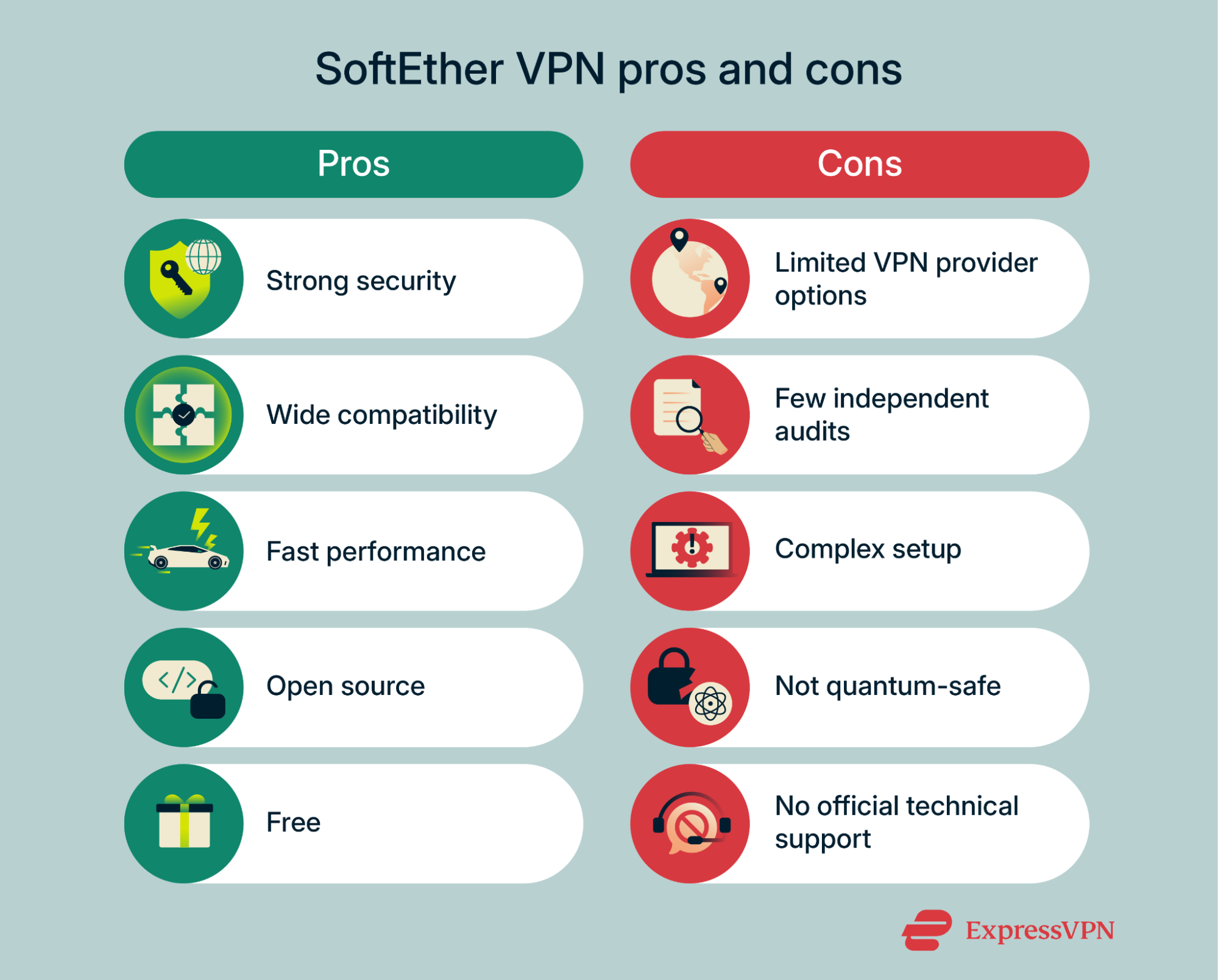
Drawbacks and limitations of SoftEther VPN
While SoftEther VPN has many strengths, it also has some important drawbacks that you should be informed of.
Limited VPN provider support
Only a few commercial VPN providers support the SoftEther VPN protocol. This means that if you want to use it, you have limited options. And if none of these options suit you and you don’t want to use volunteer-run servers, you may need to set up and host your own VPN servers. This places additional responsibilities on you, including server costs, maintenance, and ensuring reliable uptime. With more widely supported protocols, the provider can handle all of this for you, making VPN setup much quicker and simpler.
Fewer audits compared to mainstream protocols
A security audit is an independent review where experts analyze a protocol’s code and behavior to check for vulnerabilities, test its defenses, and verify that it works as claimed. Regular audits are crucial for building trust in VPN protocols, since they reveal potential weaknesses.
SoftEther has only gone through one major audit in late 2017, and while the vulnerabilities that were discovered were subsequently patched, no follow-up audits have been performed since. This makes it harder to be confident in SoftEther’s long-term security compared to more widely audited protocols. The Lightway protocol, for example, has undergone four independent audits since 2021 with the latest one occurring in October 2024.
Complicated manual setup
Another drawback of SoftEther VPN is that setting up a connection requires you to install additional components and configure them manually, which can be challenging and time-consuming, especially for those without technical expertise.
Commercial VPNs are much easier to use. Typically, all you have to do is download and install the VPN app of your choice from the official website, launch the client, and then click the Connect button: the entire process takes about 5 minutes.
Not quantum-safe
SoftEther VPN doesn’t provide post-quantum protection. This means that a sufficiently powerful quantum computer may be able to crack its encryption algorithms and expose your data. Such a computer doesn’t exist yet, but it could arrive as early as within the next 10 to 15 years.
Furthermore, even before such machines exist, your data could be vulnerable to “harvest now, decrypt later” tactics, where threat actors record encrypted traffic today with the intention of decrypting it later once technology makes it possible. For data that must remain confidential for many years, this presents a real risk. (In contrast, some VPNs, including ExpressVPN, have begun addressing this emerging threat by integrating post-quantum protection into their protocols.)
No official technical support
While SoftEther VPN does offer extensive documentation and step-by-step tutorials on its website, support is only provided via the community forum, where users can share solutions and project members may occasionally respond. This makes SoftEther better suited for technically confident users who can troubleshoot on their own. By contrast, many commercial VPNs offer 24/7 live chat, so you can get immediate assistance whenever problems arise.
How to install and configure SoftEther VPN
SoftEther VPN doesn’t come with pre-hosted servers like commercial VPN services. To use it, you can either set up your own VPN server or connect to VPN Gate, a network of free public VPN servers that run on the SoftEther VPN software. VPN Gate was created as a research project at the University of Tsukuba, the same institution behind SoftEther, and it allows anyone to access volunteer-hosted SoftEther servers around the world.
Below, we’ll cover the main steps for getting started with SoftEther VPN, including system requirements, installation, basic configuration, and optional security settings like enabling a firewall.
SoftEther prerequisites and system requirements
There aren’t many prerequisites or system requirements to connect to VPN Gate public servers using SoftEther VPN. You just need a Windows, macOS, iOS, or Android device with a stable internet connection.
Windows users can use the SoftEther VPN client for one-click connections, while macOS, iOS, and Android users need to configure the connection manually, either via the OS’s built-in L2TP/IPsec client or a third-party OpenVPN client.
If you want to set up your own VPN server, you’ll need:
- A compatible device to act as the server. SoftEther VPN supports Windows, Linux, FreeBSD, and Solaris for server installations, but Ubuntu is the recommended environment.
- The required software and libraries for installing a VPN server on a Linux operating system.
- A stable internet connection and a publicly routable IPv4 or IPv6 address to allow clients (devices) to connect.
- Administrative access to install and configure the server software.
- Enough CPU and RAM to handle the expected number of clients.
- At least 10GB of free space on the /var/ partition for logs and configuration files.
- Secure Shell (SSH) access for remote management.
- To configure user accounts, security options, and open any necessary ports in your firewall for VPN traffic.
Step-by-step installation guide
Follow these SoftEther VPN setup guides to connect to VPN Gate servers on a Windows device or use SoftEther as your self-hosted VPN solution on a Linux device.
Connecting to VPN Gate (Windows)
- Visit the VPN Gate website and download the SoftEther VPN Client with the VPN Gate Client Plug-in.
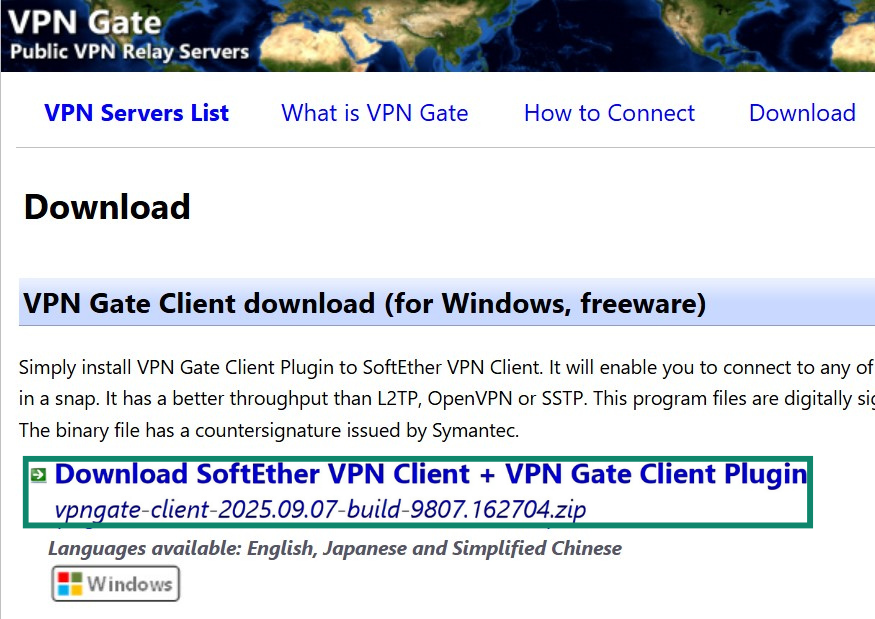
- Extract the contents of the ZIP file and run the setup program called vpngate-client-.
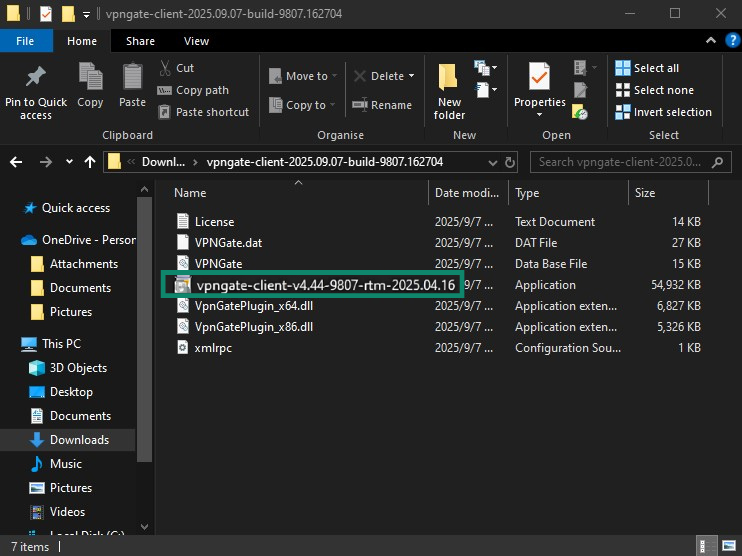
- Follow the on-screen instructions provided by the installation wizard. When asked to select software components to install, choose SoftEther VPN Client.
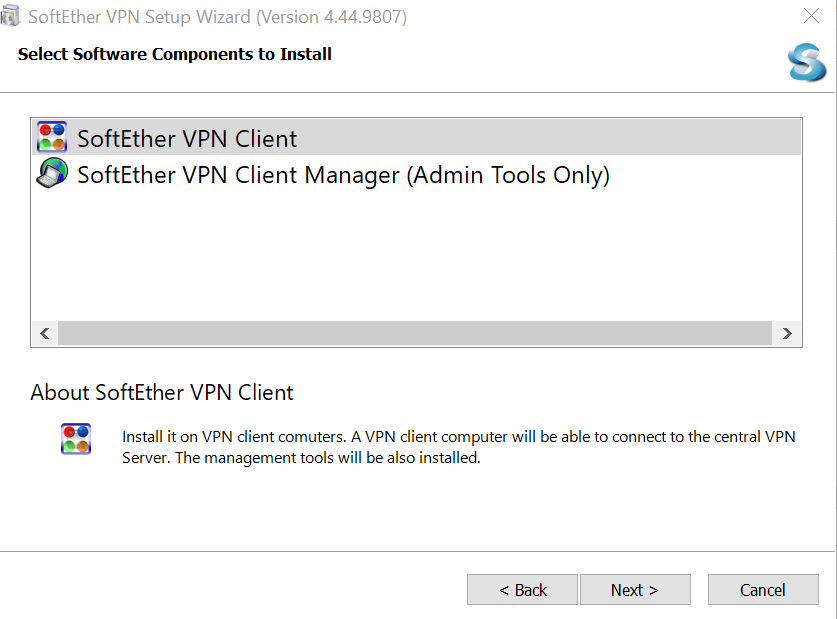
- In the SoftEther VPN Client Manager, double-click on VPN Gate Public VPN Relay Servers.
- A screen will pop up showing a list of currently available servers. Choose one from the list and click Connect to the VPN Server.
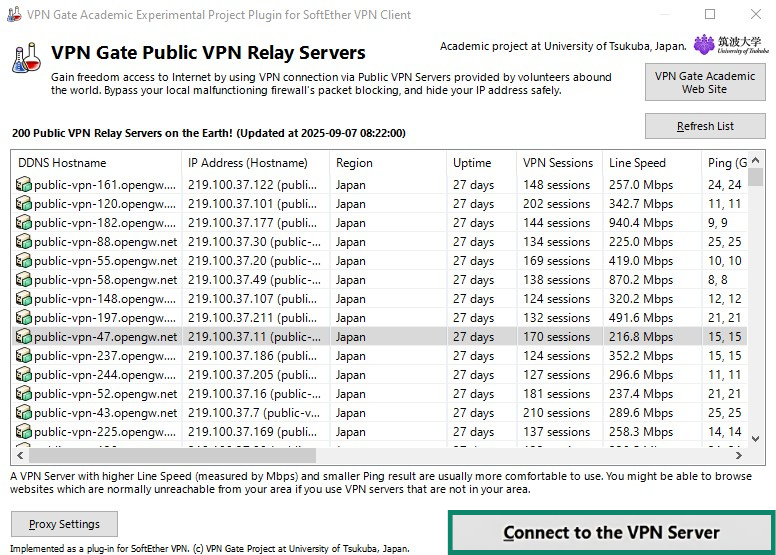
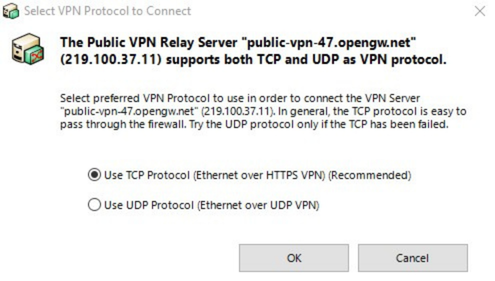
- If the selected server supports both Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) protocols, you'll be asked to choose one of them. If you’re not sure what the difference is, choose TCP. And that’s it! Your device is now connected to the VPN server.
Self-hosting SoftEther VPN (Linux)
- Download the latest SoftEther VPN Server package from the official site, extract the package, and navigate to the extracted vpnserver directory:
tar xzvf softether-vpnserver-*.tar.gz
cd vpnserver
- Compile the server software by running the make command. Follow the prompts in the terminal. After compilation is complete, move the vpnserver directory to /usr/local for system-wide use and navigate into it:
make
sudo mv vpnserver /usr/local/
cd /usr/local/vpnserver
- Secure the server files by setting the proper permissions for the executable and supporting files:
sudo chmod 600 *
sudo chmod 700 vpnserver
sudo chmod 700 vpncmd
- Launch the VPN server in the background and verify that it is running correctly:
sudo ./vpnserver start
sudo ./vpnserver status
- Access the command-line management tool to set an admin password and prepare the server for configuration. Launch the tool and select option 1 for server management. Follow the prompts to create a secure admin password:
sudo ./vpncmd
Configuration walkthrough for beginners
Once your SoftEther VPN server is installed and running, the next step is to configure it for use. Begin by accessing the command-line management tool:
./vpncmd
Choose option 1 to manage the VPN Server and enter the admin password you set during installation.
The first configuration task is to create a Virtual Hub. A Virtual Hub acts as a logical VPN network where your users will connect. Use the HubCreate command and follow the prompts to set a hub name and a password to secure it:
HubCreate MyHub
Next, set the newly created hub as active:
Hub MyHub
You can now add user accounts for clients who will connect to your VPN. Each user requires a username and password. Create a user with:
UserCreate username
Then assign that user a password:
UserPasswordSet username
If you intend to manage the server remotely, enable the management function and configure the listening port in vpncmd. Make sure your firewall allows connections to this port. For beginners, keeping the default port is sufficient while learning the basics.
Finally, verify that the hub is active and users are configured correctly. You can start and stop the hub, check connection status, and monitor logs through vpncmd. At this stage, your server is ready for clients to connect using the SoftEther VPN Client software with the hub name, username, and password you set.
Enabling a firewall for security
When self-hosting a SoftEther VPN server, configuring a firewall is essential to protect your network from unauthorized access. Begin by restricting inbound traffic to only the necessary ports for your VPN protocols. For SoftEther, this typically means allowing TCP port 443. If you're using other protocols like L2TP/IPsec, ensure their respective ports are open. It's advisable to block all other ports to minimize potential attack vectors.
Additionally, consider implementing rate limiting to mitigate brute-force attacks and logging to monitor suspicious activities. These measures enhance your ability to detect and respond to potential security threats promptly.
SoftEther VPN vs. other protocols
Here are the main differences between the SoftEther VPN protocol and the most widely used alternatives.
SoftEther VPN vs. OpenVPN
SoftEther has better speed and throughput. However, OpenVPN allows you to choose between UDP and TCP, which makes it more flexible. Users can choose UDP for faster speeds and TCP for more reliable performance under challenging network conditions.
Another key advantage of OpenVPN is its maturity and widespread adoption, which means it's been extensively tested in real-world environments. It also has a larger community, which contributes to ongoing protocol improvements and security reviews. All of this increases confidence in its long-term security.
SoftEther vs. WireGuard
Like SoftEther, OpenVPN, and Lightway, WireGuard is an open-source protocol. However, it has a much lighter codebase than SoftEther. This makes it easier to audit, less resource-intensive, and less prone to vulnerabilities. WireGuard also enjoys broader adoption and has undergone more extensive testing and review.
SoftEther vs. IKEv2/IPSec
Internet Key Exchange version 2 with Internet Protocol Security (IKEv2/IPsec) relies on well-known ports/protocols (500, 4500, Encapsulating Security Payload, or ESP), which are more likely to be blocked by firewalls. But it’s generally more stable than SoftEther when switching networks, making it well-suited for mobile users who frequently move between Wi-Fi and cellular connections.
SoftEther vs. PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is an outdated VPN protocol that’s no longer considered secure. It’s also slower and closed-source.
SoftEther vs. L2TP/IPSec
A well-configured Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) setup can be as secure as a basic SoftEther VPN setup, but the actual security depends on implementation details and the chosen cryptographic suites for features like UDP encapsulation and forward secrecy, both of which SoftEther provides by default. L2TP/IPSec is also slower and more likely to be blocked by firewalls. Many top VPN providers have dropped support for it, and in 2024, it was also deprecated by Microsoft.
SoftEther vs. SSTP
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is a secure VPN protocol that uses port 443, the same port as HTTPS and SoftEther. But it’s similarly unpopular with commercial VPN providers as SoftEther, and unlike SoftEther, it can only be used on Windows devices. Additionally, because it’s closed-source and owned by Microsoft, it’s not as well-trusted.
SoftEther vs. Lightway
Lightway, ExpressVPN’s proprietary VPN protocol, has a more compact codebase, has undergone multiple independent audits, and, unlike SoftEther, it includes post-quantum protection.
Lightway also allows you to choose between TCP and UDP, providing extra flexibility, handles network changes seamlessly, and can operate over port 443, disguising VPN traffic as HTTPS traffic just like SoftEther.
Moreover, Lightway is much easier to set up and use thanks to built-in support on a commercial VPN app and gives users access to more features and more server locations.
However, unlike SoftEther, Lightway is a proprietary protocol only available to ExpressVPN users.
Is SoftEther the right VPN solution for you?
SoftEther VPN is a powerful and versatile VPN software suite known for its strong security, impressive speed, and ability to bypass firewalls and network restrictions. Its multi-platform compatibility and open-source nature make it especially appealing to tech-savvy users, VPN enthusiasts, and organizations that prefer to self-host or manage their own VPN infrastructure.
However, SoftEther remains a niche option compared to more widely adopted protocols like OpenVPN, WireGuard, or Lightway. It has fewer audits, less commercial support, and is much more complex for setup and configuration.
SoftEther is best suited for users who are comfortable managing their own VPN setup. For general consumers or businesses seeking ready-to-use solutions with extensive support and proven reliability, more mainstream protocols are likely a better fit.
In short, SoftEther VPN excels in specialized scenarios where its unique features shine, but it’s not the default choice for most typical VPN users.
FAQ: Common questions about SoftEther VPN
Is SoftEther VPN safe to use?
Yes, SoftEther VPN is safe to use. It’s an academic project from the University of Tsukuba in Japan, and it provides strong 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption, which makes data unreadable to third parties. It’s also an open-source project, so anyone can look at its code to check for vulnerabilities.
Is SoftEther VPN free?
Yes, SoftEther VPN client, bridge, and server software are all completely free to use. SoftEther also has an extended plug-in called VPN Gate that you can use to connect to volunteer-run servers worldwide at no charge.
What is SoftEther VPN used for?
Like other VPNs, SoftEther helps secure your internet traffic through encryption, which scrambles the data so it’s unreadable to third parties, including internet service providers (ISPs) and cybercriminals. Compared to some other VPN protocols, SoftEther stands out for its ability to get through firewalls and network restrictions.
Can I use SoftEther with ExpressVPN?
No, ExpressVPN doesn’t support the SoftEther VPN protocol. In fact, limited VPN provider support is one of SoftEther’s major drawbacks.
Is SoftEther VPN good for torrenting or streaming?
The SoftEther VPN protocol can deliver fast speeds for torrenting and streaming, but it’s not a practical option because few commercial VPN providers support it.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN