No network connection: Why it happens and how to fix it

Few things are more frustrating than seeing a “no network connection” message when you need to get online. This issue can happen on any device, from phones to laptops, and may manifest as Wi-Fi connected but no internet, intermittent outages, or a complete loss of access.
Understanding why your connection fails is the first step to fixing it. In this guide, you will find clear explanations of common causes, practical troubleshooting steps, and expert tips to restore your internet quickly. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, these solutions will help you identify the problem and get online without unnecessary confusion or delay.
Why is my internet not working?
Your internet may stop working for several reasons. It could be a problem with your internet service provider (ISP), an issue with your home network equipment, or something on your device like outdated software.
Sometimes the issue is temporary, like a brief outage, and other times it needs troubleshooting. Understanding the cause helps you fix it faster.
What does “no network connection” mean?
“No network connection” usually means your device can’t reach the internet. You might still be connected to Wi-Fi or mobile data, but your device can’t send or receive information online.
Why does my Wi-Fi say “connected but no internet”?
If your Wi-Fi shows as connected but the internet doesn’t work, it means your device is communicating with the router, but the router can’t reach the wider internet.
Common causes of internet issues
Internet problems usually fall into a few categories. They can be caused by your ISP, hardware like routers and modems, faulty cables, or software issues on your device. Knowing the common causes helps you target the right fix without unnecessary steps.
- ISP problems: Sometimes your internet stops working because of issues with your ISP. The cause could be maintenance, outages, or technical problems on their end.
- Router and modem configuration issues: These devices manage your internet at home. If they are misconfigured, overloaded, or need a restart, your devices may lose connection.
- Faulty cables, hardware, or too many devices: Broken or loose cables or damaged hardware may cause issues. Additionally, too many devices connected to the same network can slow it down or block new connections.
- Outdated or missing network drivers: Your computer or device needs software called network drivers to communicate with the internet. If these drivers are outdated, missing, or corrupted, your connection can fail.
How to confirm if it’s really your internet
Before spending time troubleshooting your device, it’s important to confirm whether the problem is truly your internet. Sometimes the issue might be a single app, website, or device rather than your entire connection. Checking systematically can save time and pinpoint the real cause.
Check your internet plan and service status
Your internet might not work if there is an issue with your plan or account. Log into your ISP’s website or app to make sure your account is active and bills are paid. Also, check if your ISP has reported outages in your area.
Test other websites and apps
Sometimes a specific website or app may be down, even if your internet is fine. Try visiting multiple websites or opening different apps that require the internet. If some work while others don’t, the problem is likely with the site or app, not your connection.
Try another device
Testing another device can help you identify if the problem is with your main device or the network itself. If other devices connect without issues, the problem may be your phone, tablet, or computer. When no devices can connect, the issue is likely with your internet or router.
Run a ping test
A ping test checks whether your device can reach another computer or website online. It’s typically done using the ping command in a system’s command-line tool, such as Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on macOS and Linux.
Ping measures how long it takes for data to travel to a destination and back, showing whether your connection is working and how stable it is.
Scan for malware or viruses
Malware and viruses can interfere with your internet connection. Run a full system scan using your antivirus software. If it detects a threat, removing it may restore your connection and improve overall device performance.
Quick fixes for internet connection problems
You can quickly solve many internet issues without changing any network settings. These simple steps help you troubleshoot and restore your connection fast.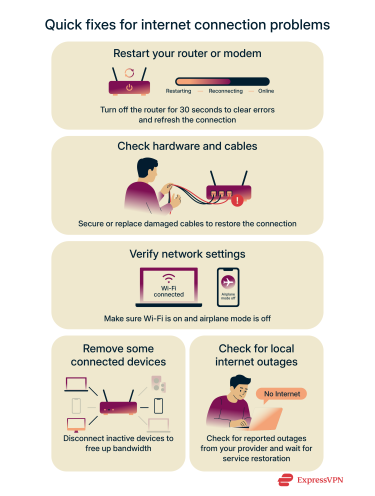
Restart your router or modem
Turning your router or modem off and on can fix most temporary connection problems that stop your devices from reaching the internet. For example, a frozen router, a modem that lost its ISP connection, or a device that’s stuck with an invalid IP address can be fixed with a restart.
Powering it down for about 30 seconds clears temporary errors and refreshes the connection to your internet service. After restarting, wait a minute or two for the devices to fully reconnect.
Check hardware and cables
Loose, damaged, or unplugged cables can stop your internet from working because they interrupt the signal traveling between your devices and your ISP. Even a slightly loose connector or a bent wire can cause your modem or router to lose its link.
Make sure all cables connecting your modem, router, and devices are secure and not frayed. If you notice any damage, replace the cables to avoid interruptions.
Verify network settings
Sometimes your device settings can block it from getting online. Check that Wi-Fi is turned on, airplane mode is off, and you’re connected to the correct network. On computers, make sure the network adapter is enabled, and on mobile devices, check the Wi-Fi or mobile data settings.
Remove some connected devices
Too many devices using your network at once can slow down or interrupt your connection. That’s because every device shares the same bandwidth, so when several are streaming, downloading, or updating at the same time, your router can get overloaded.
Try disconnecting devices that aren’t in use. This frees up bandwidth and can restore internet access for your main device.
Check for local internet outages
Your internet may be down due to issues with your ISP. Check their website, social media, or outage reporting tools to see if other people in your area are affected. If there’s an outage, you’ll need to wait for the ISP to fix it.
If you can’t reach the ISP’s website, try calling their customer support instead. You can usually find their contact details in your service contract or billing statement.
Advanced troubleshooting techniques
If quick fixes don’t restore your internet, you may need to perform a few advanced techniques. These focus on software and settings that control how your device connects to the network.
Update network drivers
Updating your network driver can resolve issues caused by software bugs, incompatibility, or corrupted drivers. It’s especially useful when your network adapter works inconsistently, like when you sometimes have internet and sometimes don’t.
Manually update on Windows
Manually updating allows you to install the exact driver you need. Here’s how:
- Press Windows + X and select Device Manager.
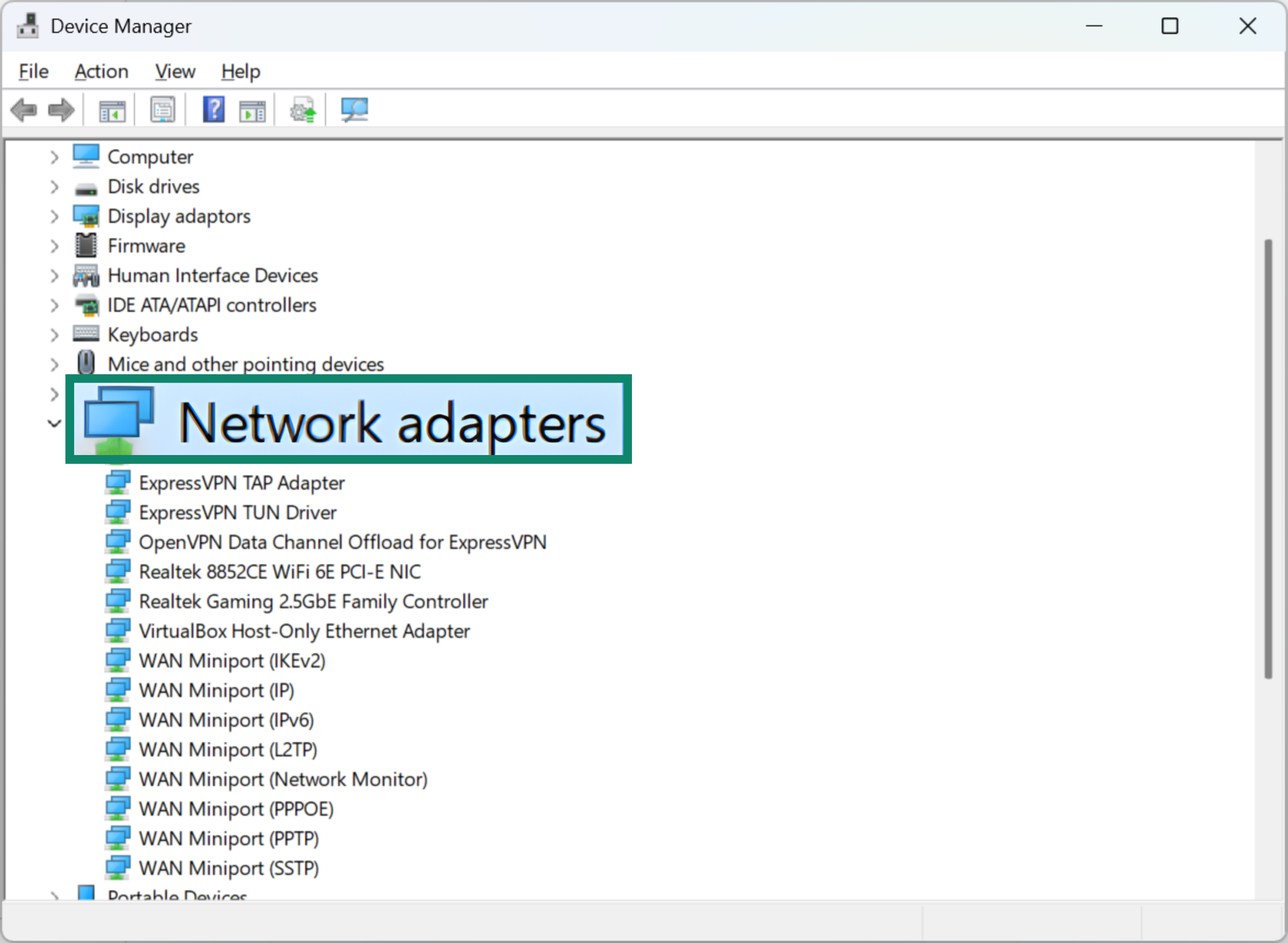
- Expand the Network adapters section and find your adapter.
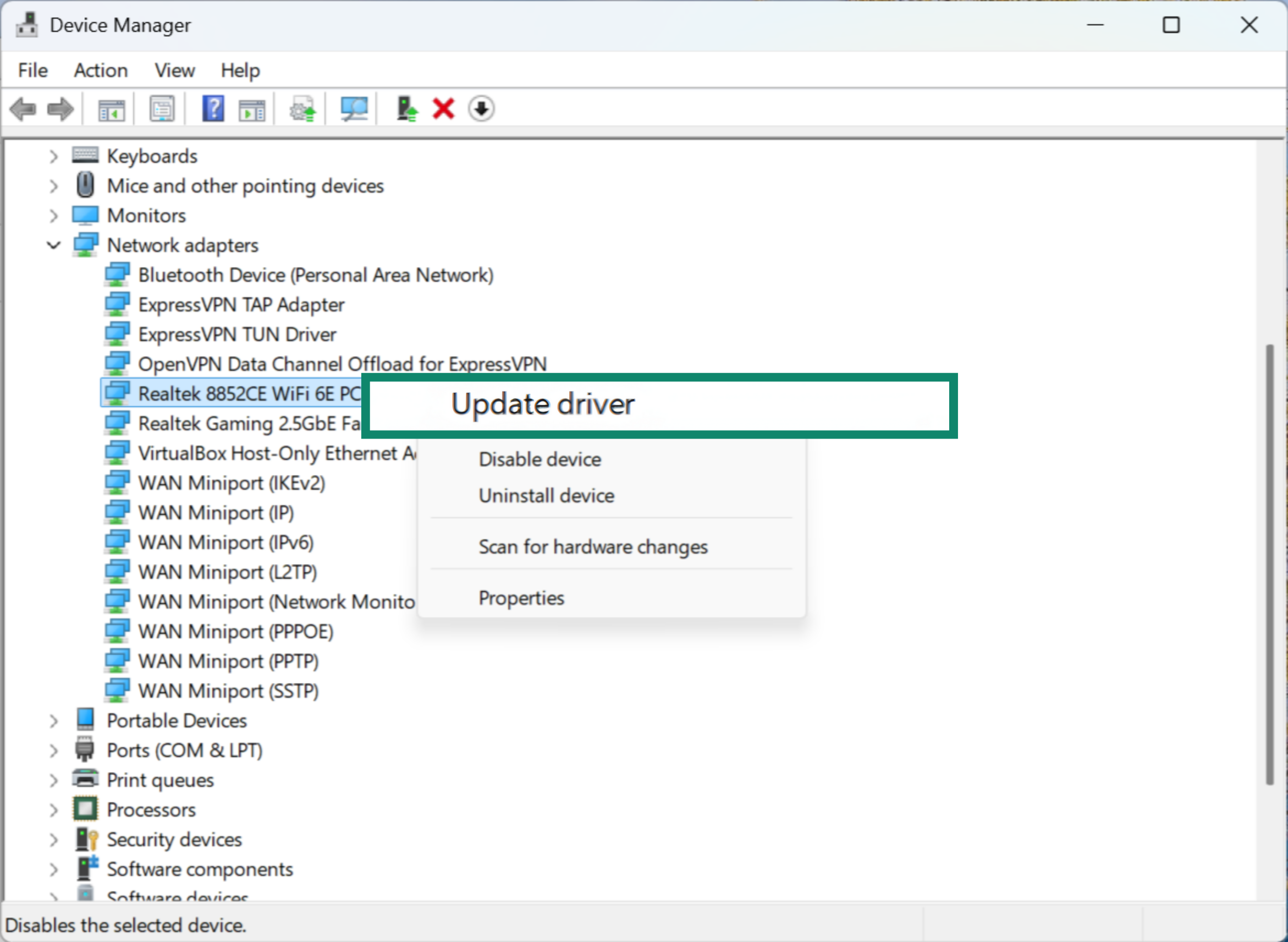
- Right-click on it and choose Update driver.
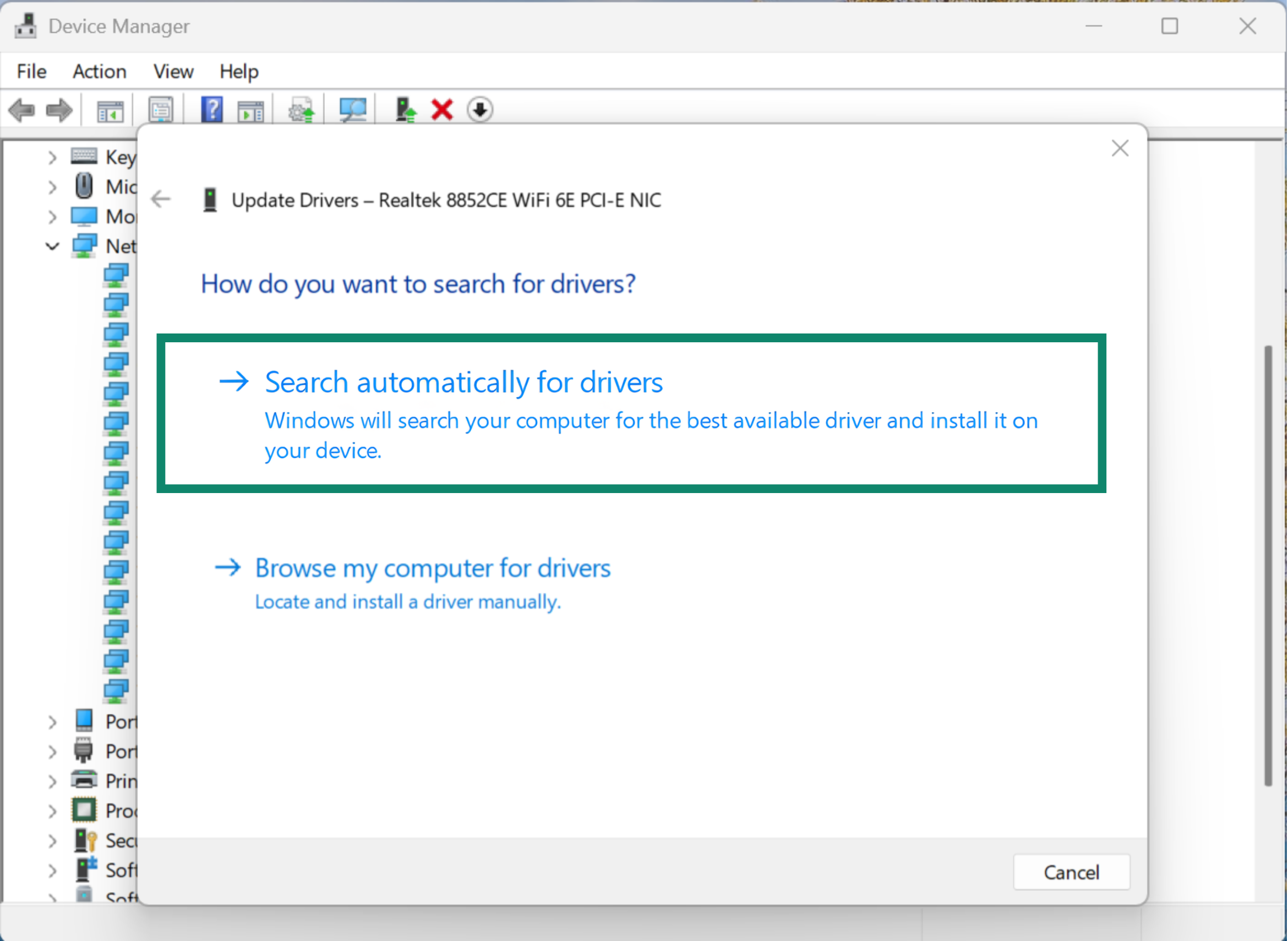
- Select Search automatically for drivers. Windows will check Microsoft’s database and install any available update. Just note that it may install an older, generic version.
- Follow the guide and restart your PC when prompted.
Automatically update drivers with tools
Depending on your device’s brand, the manufacturer may offer built-in software or downloadable tools that automatically check for and install the latest network drivers. These tools help keep your device running smoothly and maintain stable network performance without requiring manual updates.
Fix IP configuration and default gateway issues
Sometimes your device can’t connect to the internet because of IP configuration problems, where your device doesn’t have a valid address on the network, or default gateway issues, which typically happen when your device can’t reach the router that connects you to the internet. Fixing these settings can restore your connection.
Change your IP address on Windows
The simplest way to fix errors like “Ethernet does not have a valid IP configuration” or “Wi-Fi doesn’t have a valid IP configuration” is using the commands ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew. This refreshes your computer’s IP settings and requests a new address from your router.
If refreshing your IP doesn’t work, you can assign a valid IP address yourself. A static IP address means your device is using a fixed local IP address that avoids conflicts and invalid assignments.
To set a static IP address on your Windows PC, follow these steps:
- Press Windows + R and type ncpa.cpl, then press Enter.
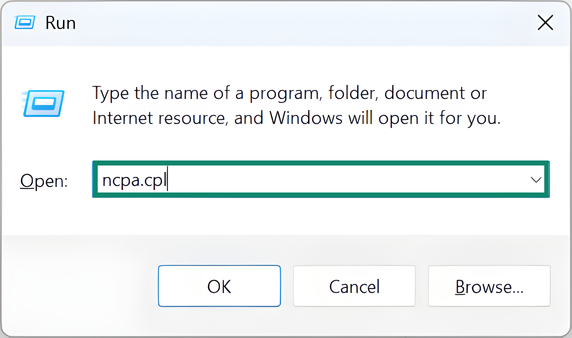
- Right-click an active network and select Properties.
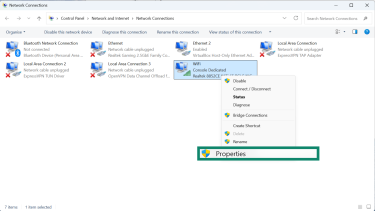
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
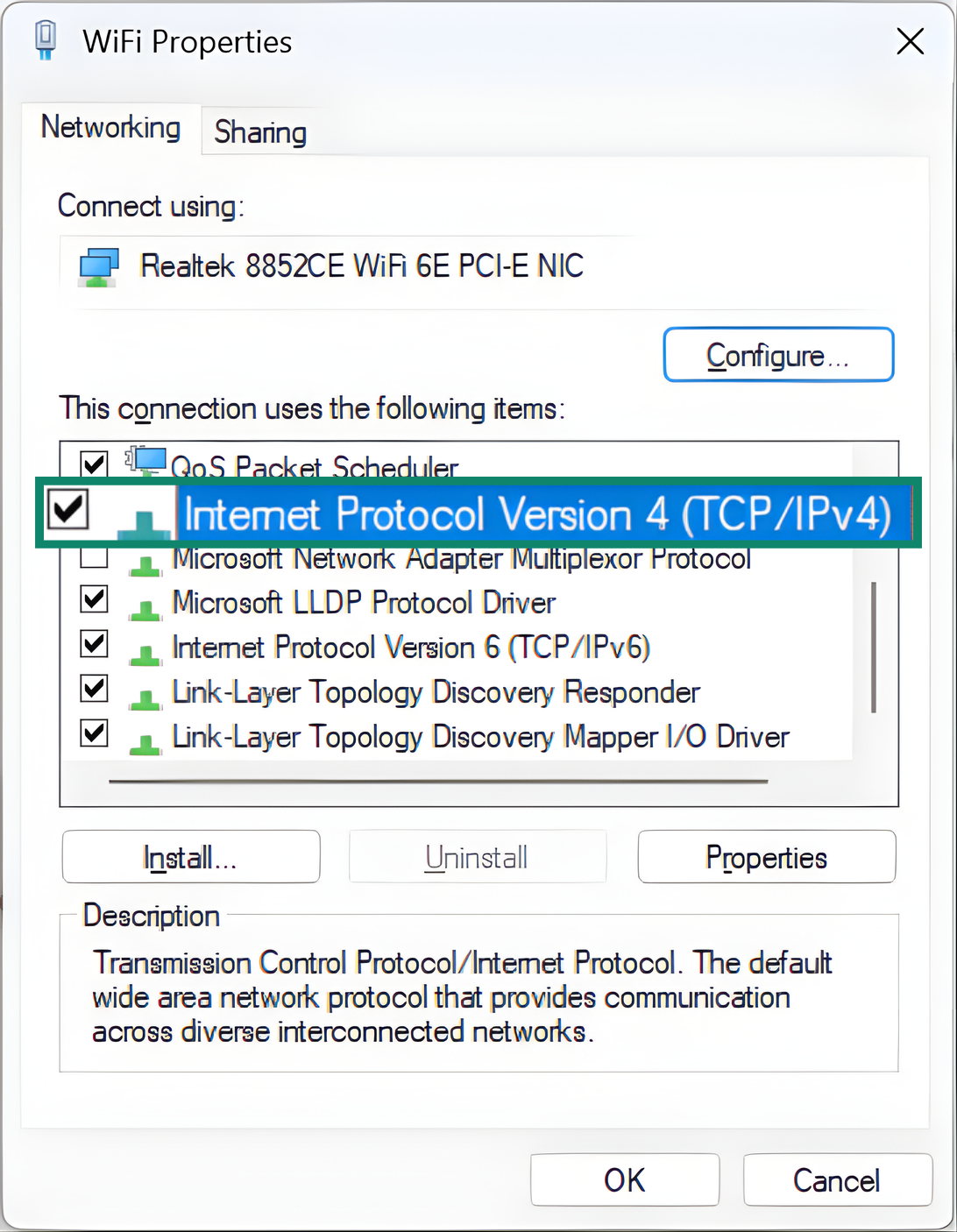
- Choose Use the following IP address and enter a new IP, subnet mask, and default gateway (your router’s IP is usually the default gateway).
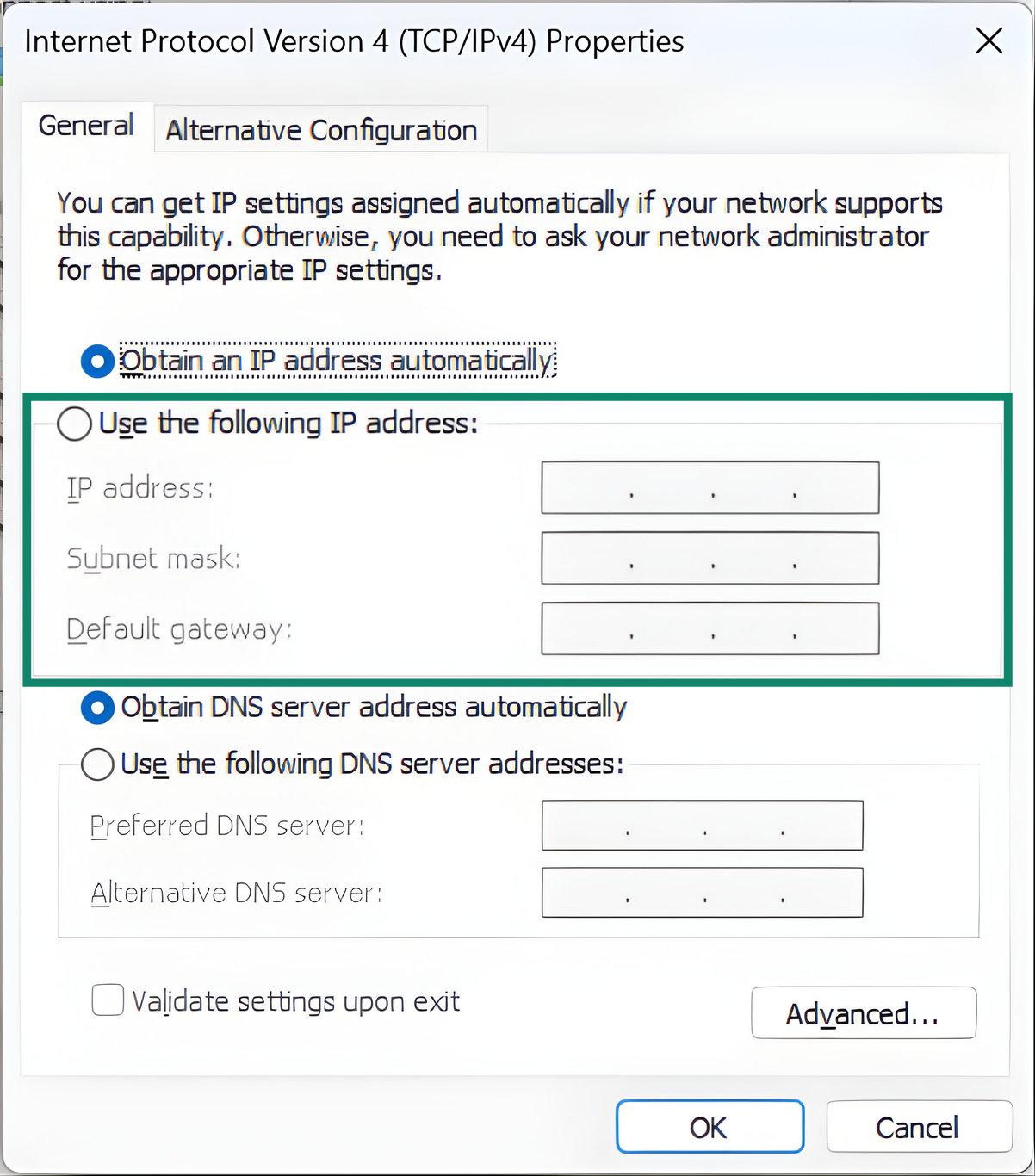
- Click OK and reconnect to your network.
Change IP address on Mac
If your Mac can connect to Wi-Fi but not the internet or shows a “Self-assigned IP” error, you can ask your router to automatically assign a new local IP to your device via the Renew DHCP lease option in System Settings.
If renewing doesn’t help, you can assign a fixed local IP manually by following the steps below:
- Open System Settings.
- Select Network.
- Select your active connection and click Details.
- Go to the TCP/IP tab.
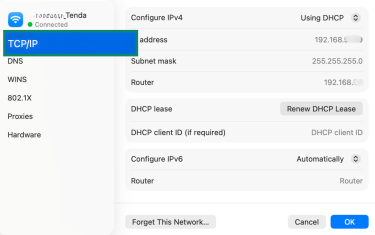
- Next to Configure IPv4, choose Manually.
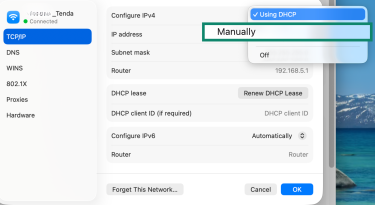
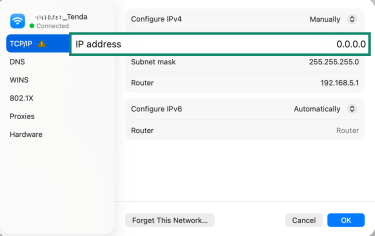
- Enter a new IP address.
Reset TCP/IP settings
Resetting Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (IP) can resolve configuration errors that prevent internet access. It removes outdated or corrupted network settings, allowing your device to receive a new configuration from the router.
On Windows
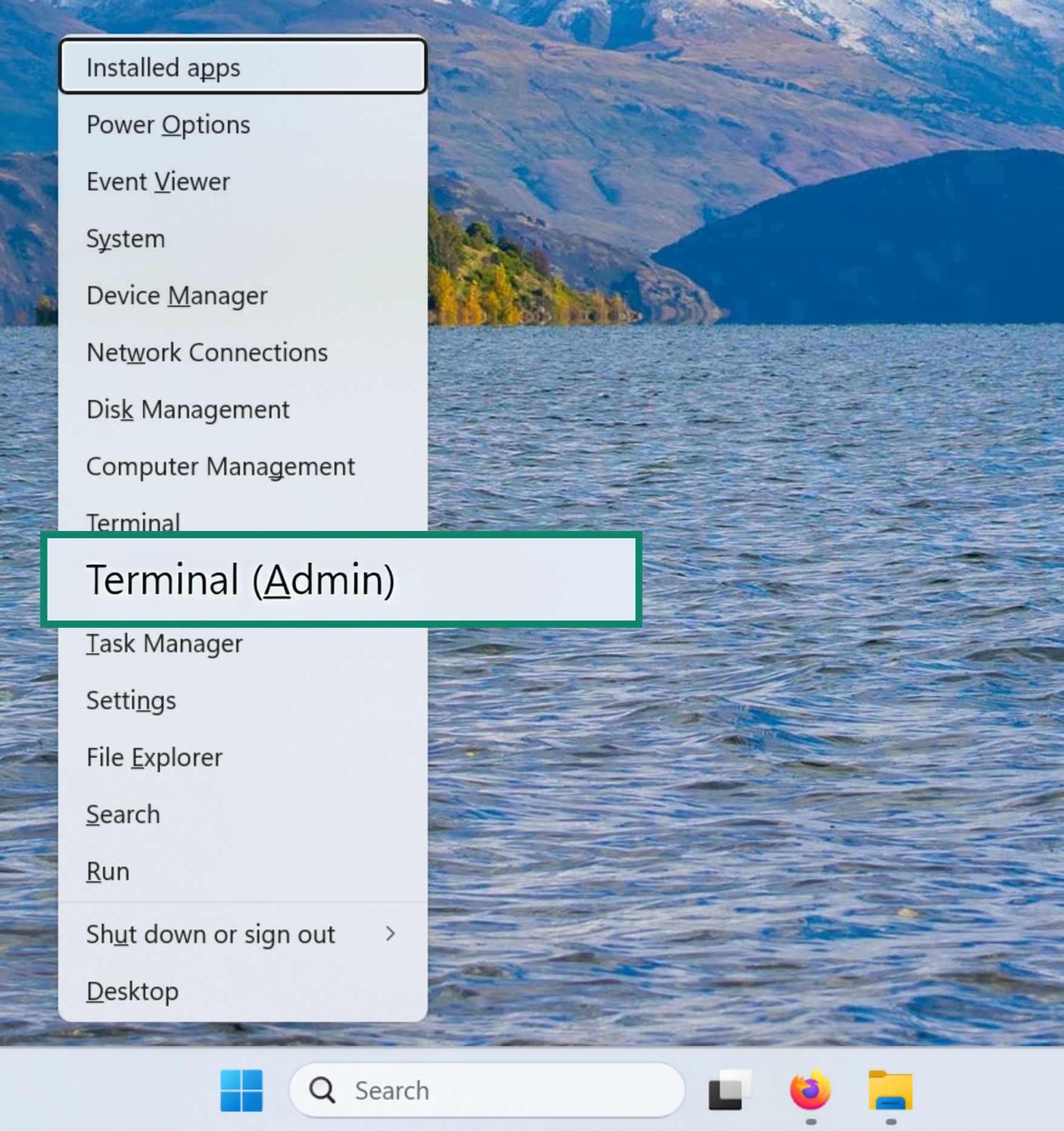
- Press Windows + X and select Terminal (Admin).
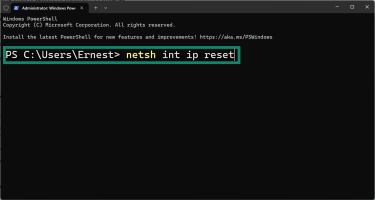
- Type netsh int ip reset and press Enter.
- Restart the computer.
On Mac
- Open System Settings.
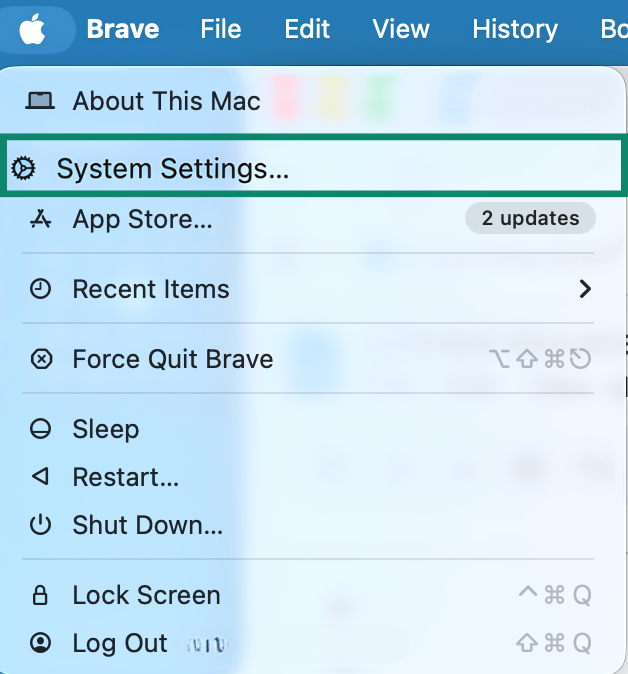
- Click on Network.
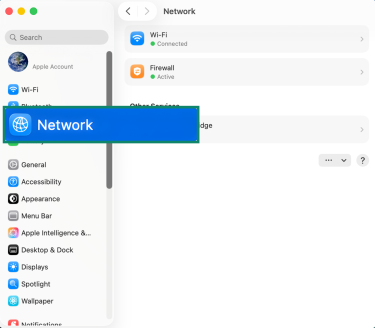
- Select the active internet connection and click Details.
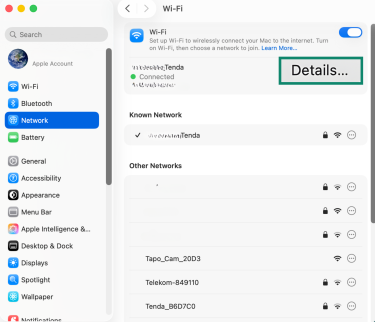
- Open the TCP/IP tab and select Renew DHCP Lease.
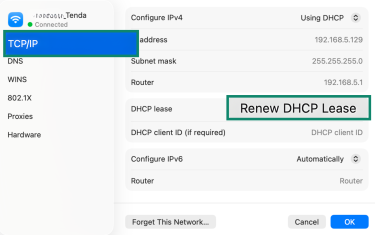
- Click OK to finish.
Correct subnet mask configuration
The subnet mask indicates which part of an IP address is the network and which part is the device. If your subnet mask was changed accidentally, your device may not be able to communicate with your router.
Note that the subnet mask for home networks is typically 255.255.255.0. Below are steps to check or correct it:
- Access your router settings by entering its IP address (usually a variation of 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1) in your browser and logging in.
- Go to Advanced Settings, select LAN Settings, and note the number next to Subnet Mask.
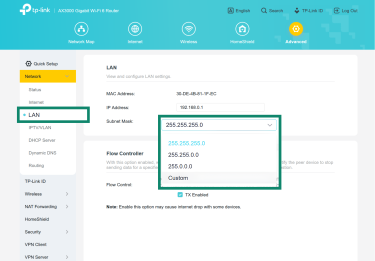
- Set your computer to use the same subnet mask as your router:
On Windows: Go to your active network’s IPv4 Properties (following steps 1–3 here), and enter the correct subnet mask.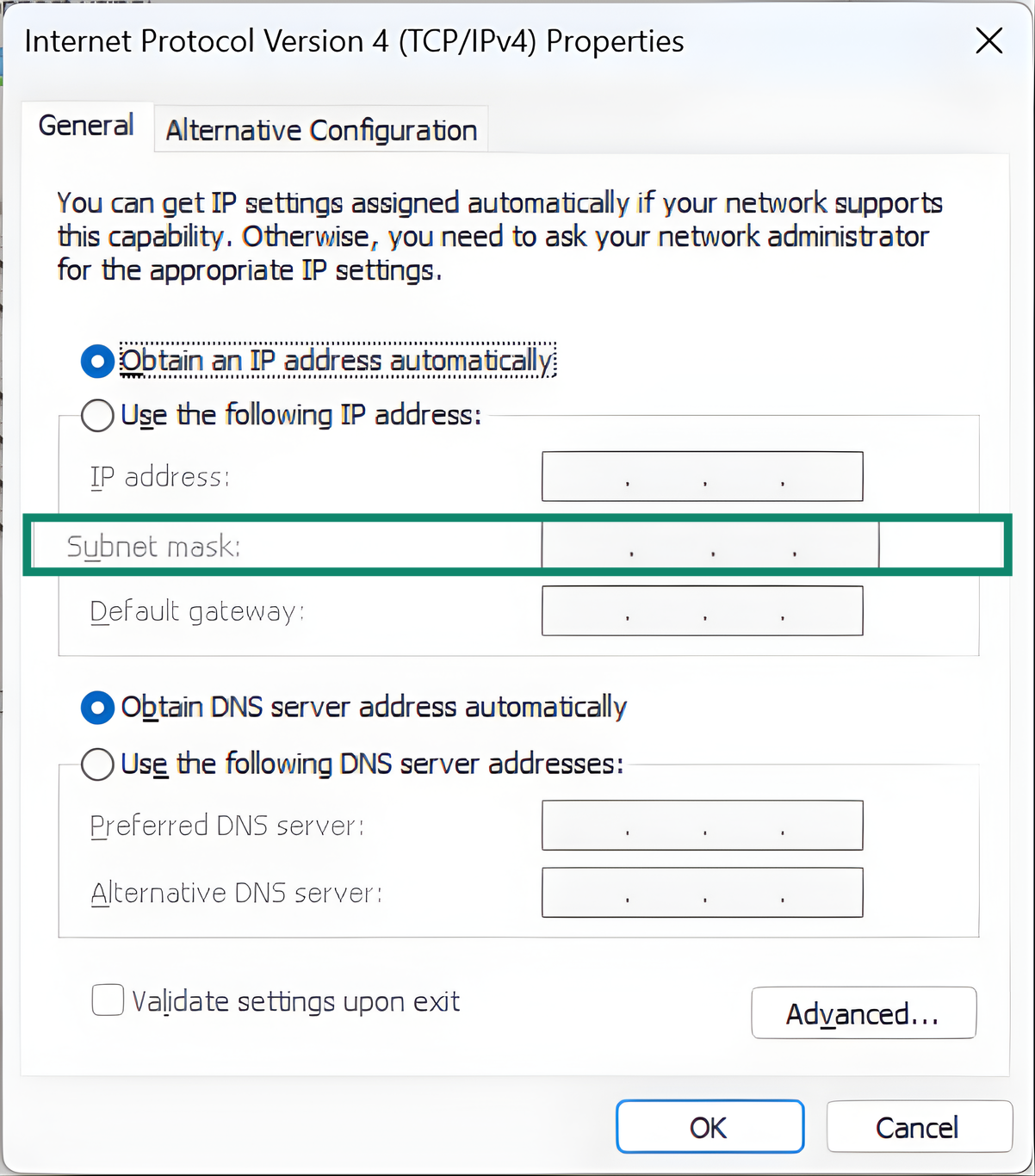
On macOS/Linux: In TCP/IP settings, select Configure IPv4, click on Manually, and enter the correct mask.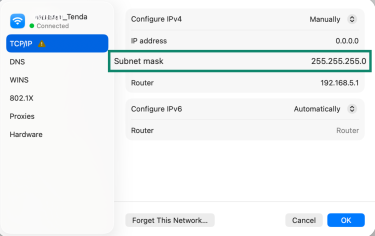
Flush the DNS cache
Flushing the DNS cache clears all the addresses your device has saved for websites and forces it to look up fresh DNS information the next time you visit a site. This can help resolve problems where certain websites won’t load, redirect incorrectly, or take unusually long to connect.
Flush DNS on Windows
- Press Windows + X and select Terminal (Admin).
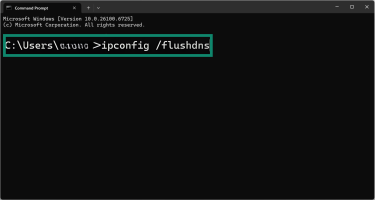
- Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.
- Restart your device.
Flush DNS on Mac
- In Finder, go to Applications, then Utilities, and open Terminal.
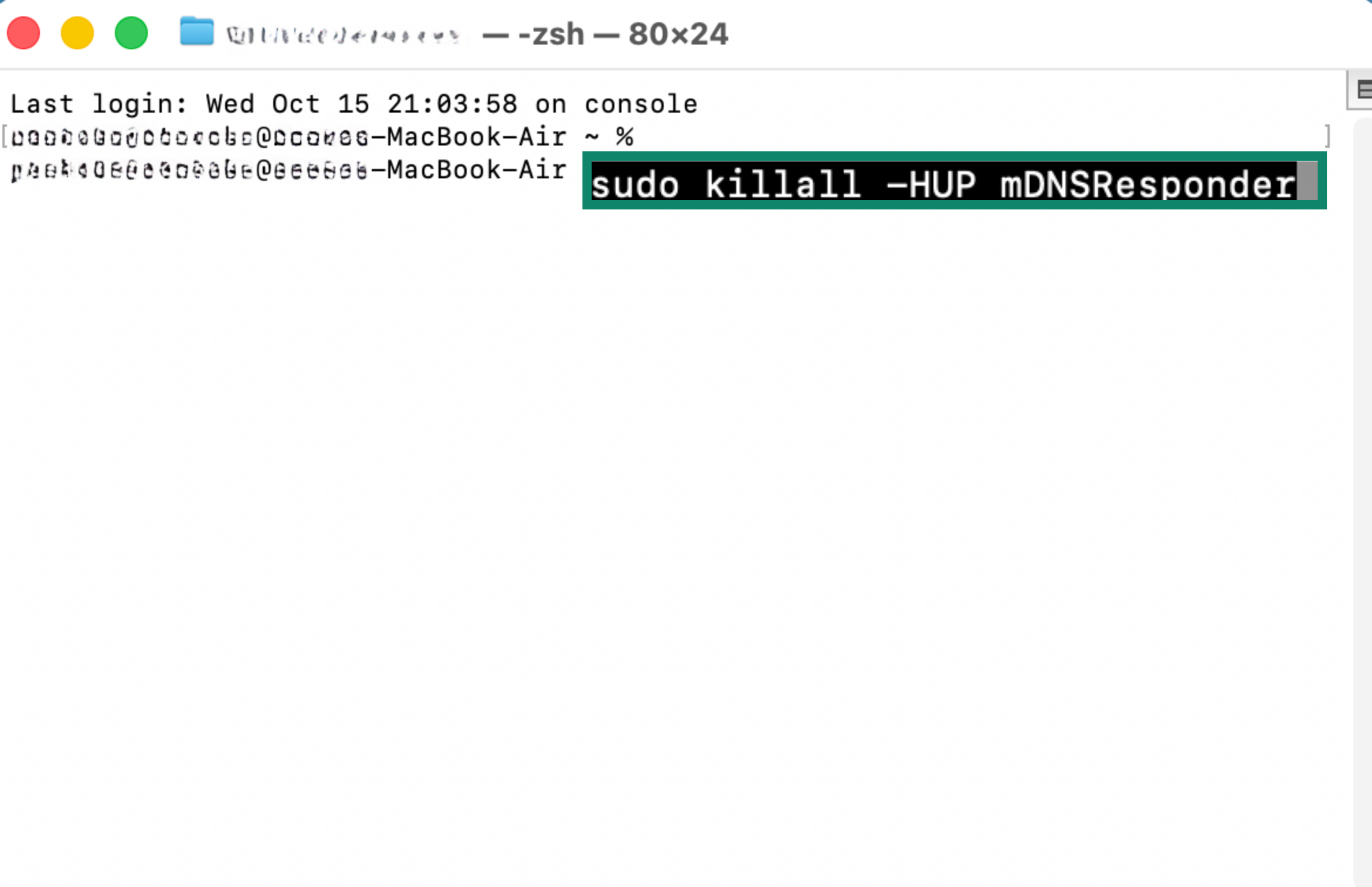
- Type sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder and press Enter.
- Enter your password if prompted, then restart your device.
Reset your network settings
Resetting network settings restores all configurations to their default state. It can resolve persistent issues caused by misconfigured settings, IP conflicts, or outdated network profiles.
Reset on Windows
- Press the Start button and open Settings.
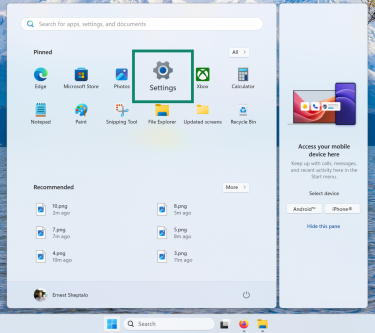
- Go to Network & Internet and click Advanced network settings.
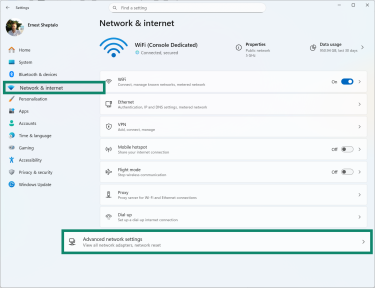
- Once inside, scroll down and select Network reset.
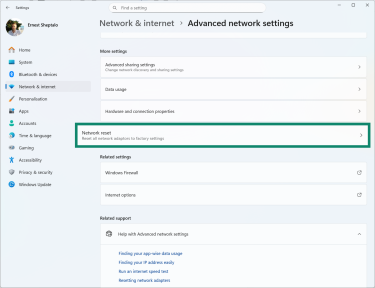
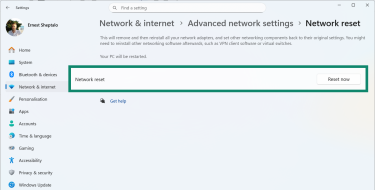
- Click Reset now and confirm.
Reset on Mac
- Go to your active network settings and click Forget This Network.
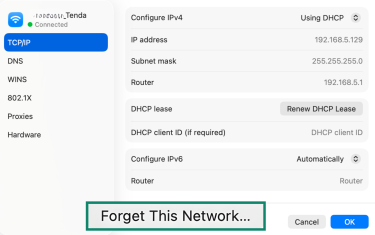
- Reconnect to your Wi-Fi by entering the password.
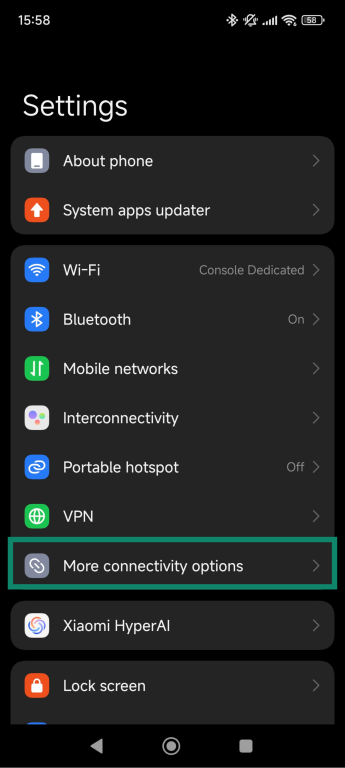
Reset on Android or iOS
On Android:
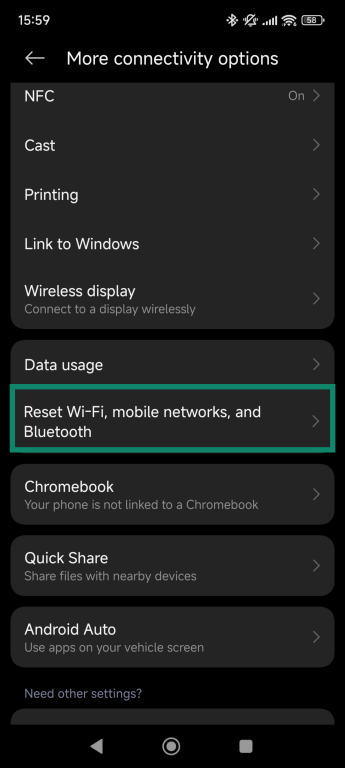
- Go to Settings and select More connectivity options.
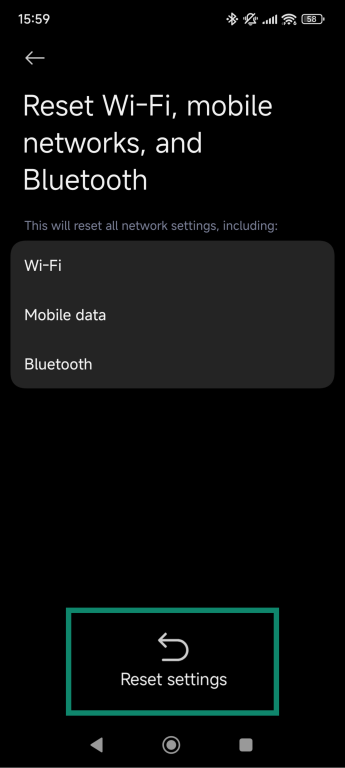
- Tap Reset Wi-Fi, mobile networks, and Bluetooth.
- Tap Reset settings to confirm and restart your phone.
On iOS:
- Go to Settings and select General.
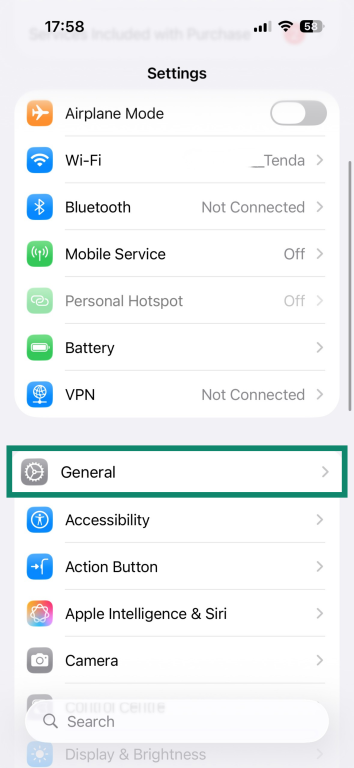
- Tap on Transfer or Reset iPhone.
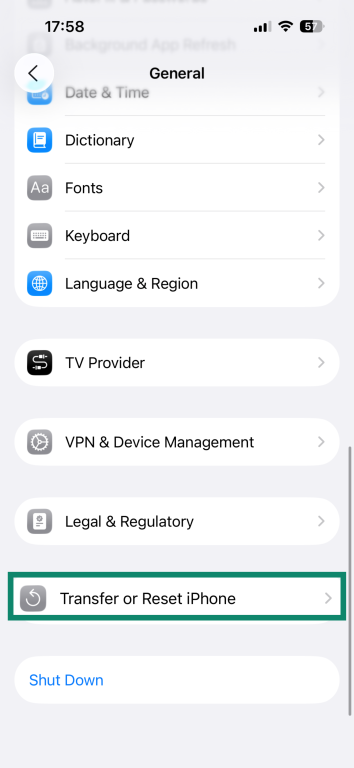
- Pick Reset.
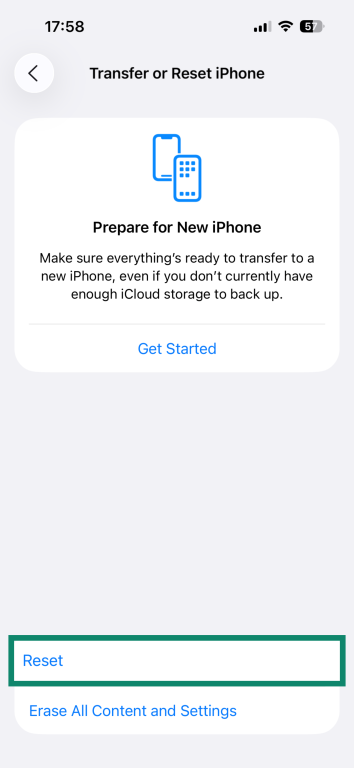
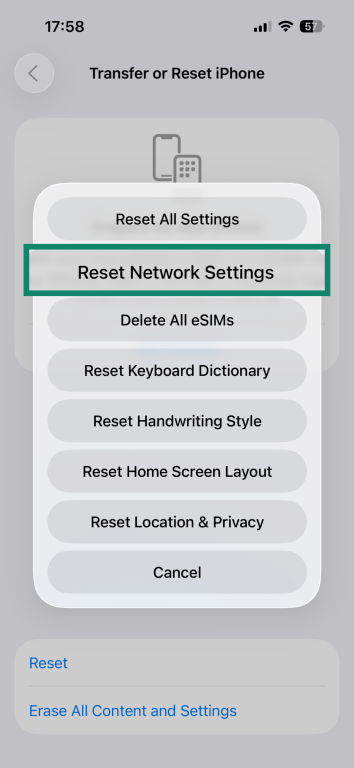
- Tap Reset Network Settings and enter your passcode.
Secure a hacked router
Routers can be targeted by cybercriminals, which may cause connection problems, stolen data, redirected traffic, or further malware attacks. By securing a compromised router, you can prevent unauthorized changes to settings such as firewall rules, which could potentially block or control your internet access. You can protect your router by following these best practices:
- Change default admin credentials: Replace the default username and password for your router’s admin panel with a strong, unique combination.
- Set a strong Wi-Fi password: Use a secure, unique password for your wireless network.
- Update router firmware: Firmware is the software that runs your router. Installing updates fixes security flaws and protects against new attacks.
- Use Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3): WPA3 is the latest Wi-Fi security standard, offering stronger encryption and better protection against hacking. If WPA3 isn’t available, use WPA2, which still provides strong wireless security.
- Disable remote management: Turn off any setting that lets someone access your router from outside your home network. This prevents hackers from controlling your router remotely.
- Enable the router’s firewall: Make sure the built-in firewall is active to block unauthorized traffic.
- Change the default DNS server: DNS translates website names into IP addresses. Using a trusted DNS server (like Google DNS, Cloudflare, or OpenDNS) can make your internet faster and prevent some types of hacking or phishing attacks.
- Turn off Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS): WPS can be vulnerable to brute-force attacks, where attackers try many password combinations to gain access. It’s also exposed to the Pixie Dust exploit, which targets weaknesses in WPS to recover your Wi-Fi password quickly. Disabling WPS is safer.
- Monitor connected devices: Remove or block any unknown devices on your network. You can also learn how to visually map devices with network mapping.
- Add a VPN to your router: A VPN encrypts your traffic and hides your IP address. You can improve privacy for all connected devices by configuring a VPN on your router.
No internet connection on Linux: Common fixes
Network issues on Linux can happen due to missing drivers, hardware problems, or incorrect settings. Common errors include “No Wi-Fi adapter found” and “Network Manager not running.” The table below summarizes solutions for each issue:
| Issue | Cause | Solutions |
| No Wi-Fi adapter found | Missing/outdated drivers, wrong configurations, or kernel issues |
|
| Network Manager not running | Service disabled or failed due to a glitch |
|
Smart TV not connecting to Wi-Fi or internet
Smart TVs are great for streaming, but connection issues can interrupt your experience. These problems often occur on LG, Samsung, and Vizio TVs.
| Issue | Cause | Solutions |
| Wi-Fi is turned off | Wi-Fi disabled or faulty Wi-Fi module |
|
| TV can’t connect to the network | Wrong password or router compatibility issue |
|
Device interference or outdated TV software can cause wireless network issues. Keep microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors away from the TV and router. If problems continue, connect the TV directly to the router using an Ethernet cable for a stable connection.
Fixing internet connection issues on gaming consoles (Xbox, PlayStation, Switch)
Network problems on gaming consoles are common but often easy to fix. The table below summarizes typical issues, their causes, and simple solutions to help you restore your connection quickly.
| Console | Issue | Solutions |
| Xbox | Can’t connect to internet or Xbox Live |
|
| PlayStation 4/5 | Connectivity errors due to PSN maintenance or local network issues |
|
| Nintendo Switch 1/2 | Wi-Fi problems from distance, interference, or crowded networks |
|
Alternative solutions when internet is not working
If your main internet connection is down, there are ways to stay online temporarily. These alternatives can help you continue working, browsing, or communicating until the main issue is resolved.
Use mobile data or tethering
If you have a smartphone with a data plan, you can use it to access the internet. You can connect your phone directly to your device using a USB cable, Bluetooth, or by creating a personal Wi-Fi hotspot. This is called tethering and works well for short-term internet access. Learn more in our dedicated guide to network connections.
Connect to public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks, like those in cafes, libraries, or stores, can be used as a temporary solution. Make sure to choose trusted locations and avoid entering sensitive information on unsecured networks. Public Wi-Fi can help you stay connected while your home's internet is down.
Use a virtual private network (VPN)
Some ISPs may slow down your connection to a crawl when you stream and game, or in some cases, take inefficient routes to certain websites. This can leave you with lag, buffering, or random connection drops. A VPN helps by encrypting your traffic and sending it through its own VPN servers.
The encryption hides your online activities from your ISP or network administrator, which makes it harder to throttle certain types of traffic. At the same time, the VPN routes your data through a VPN server instead of your ISP’s, giving it a different route across the internet and allowing it to bypass the routing problems that may sometimes cause slow or unstable connections. ExpressVPN uses Lightway, which is built for speed, so you get strong privacy and a steady connection.
FAQ: Common questions about no network connection
What does “Ethernet doesn’t have a valid IP configuration” mean?
The “Ethernet doesn’t have a valid IP configuration” error means your computer can’t get a proper network address from the router. This can happen due to incorrect network settings, driver issues, or conflicts with other devices on the network. When this occurs, your PC may show limited or no internet access even though the Ethernet cable is connected. To fix it, you can restart your router and renew the IP address.
Why does my computer say “self-assigned IP address”?
A “self-assigned IP address” error occurs when your device can’t get an IP address from the router and assigns one automatically. This usually happens because of network adapter problems or temporary router glitches. With a self-assigned IP, your computer may connect to the local network but can’t access the internet. Common solutions include restarting the router, resetting the network adapter, or manually configuring an IP address.
How do I fix “Mobile network not available” on Android?
A “Mobile network not available” error on Android means your phone can’t detect or connect to a cellular network. This can be caused by poor signal, SIM card issues, incorrect network settings, or temporary carrier problems. To resolve it, try restarting your device or checking your SIM card for any physical damage.
Why does my iPhone say “No SIM” or “Invalid SIM”?
A “No SIM” or “Invalid SIM” error on an iPhone means your device isn’t detecting the SIM card properly. This can happen if the SIM is loose, damaged, or if your network settings are misconfigured. Try removing and reinserting the SIM, cleaning the tray, or resetting network settings.
You can also test another SIM card to see if the issue is with the phone itself. If it turns out to be a hardware problem or your physical SIM isn’t working, you could try using an eSIM instead, if your iPhone supports this. It's quick to set up, doesn’t require a physical card, and can get you connected instantly.
What are the most common network issues in apps like Roblox or Zoom?
Network issues in apps like Roblox or Zoom usually happen because of slow internet, weak Wi-Fi, or blocked network ports. These problems can lead to lag, sudden disconnections, or failed logins. To fix them, test your internet speed and use a wired connection if you can. It also helps to check your firewall or antivirus settings to make sure they aren’t blocking the app’s internet access.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN